carboxylate ir stretch
Hyrdogen-Bonded Hydroxyl Groups in the Introduction to IR Spectra for more information. A widely used principle is that shifts in the wavenumber of carboxylate stretching modes upon bonding with a metal.
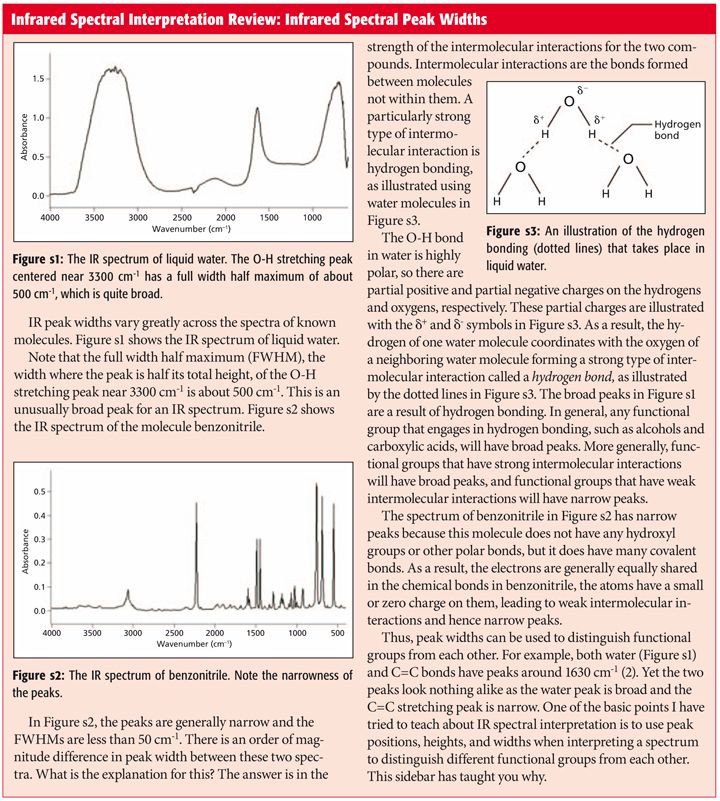
The C O Bond Part Iii Carboxylic Acids
The spectrum of a CCl 4 solution of propionic acid propanoic acid shown below is illustrative.

. The bands corresponding to the coordinated modes structures II III and IV are situated at different frequencies relative to values for the free carboxylate ion. This absorption overlaps the sharper C-H stretching. The frequency of the carboxylate stretching vibration near 1550 cm.
Now carboxylates with different metal atoms will have different infrared spectra because they have different chemical. A typical ketone or a carboxylic acid both show a strong CO stretch at around 1715 cm -1. 1 in the benzoate ion ranges in the derivatives from 1500 cm.
The infrared spectra of six aqueous carboxylate anions have been calculated at the M05-2Xcc-pVTZ level of theory with the SMD solvent model and validated against experimental data from the literature over the region of 1700 cm 1 to 1250 cm 1. Its value is 1635 for ester and 1681 for ketone CCSD6-311G dp or 17661848 ωB97XDaug-cc-pvQZ. We report the first IR spectroscopic observation of carboxylate stretching modes in free space ie in the complete absence of solvent or counterions.
Primary amines produce two N-H stretch. A linear standard curve using anhydrous sodium salicylate has been obtained from the plot of carboxylate COO concentration vs. What is the IR frequency for alkene CH stretching.
The C-H wags of alkenes fall in a similar range between 1000 and 600. This region corresponds to the stretching modes of the carboxylate group and is often interrogated when probing bonding. The carbonyl stretch is rather sensitive towards its environment which provides a valuable diagnostic tool.
A widely used principle is that shifts in the wavenumber of carboxylate stretching modes upon bonding with a metal center can be used to infer if the geometry of the bonding is monodentate or bidentate. It is reported that the first IR spectroscopic observation of carboxylate stretching modes in free space ie in the complete absence of solvent or counterions is reported. IR carboxylate stretching modes are widely used to infer if the geometry of the bonding is monodentate or bidentate.
The O-H stretching absorption for such dimers is very strong and broad extending from 2500 to 3300 cm -1. 1 in the zwitterion of picolinic acid being strongly influenced by the polar effects of substituents. The average of 1700 and 1200 is 1450 close to where the carboxylate stretching peaks fall.
We report the first IR spectroscopic observation of carboxylate stretching modes in free space ie in the complete absence of solvent or counterions. 1 in the dianion of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid to 1650 cm. To summarize then the IR spectra of alkenes are characterized by one or more C-H stretching peaks between 3100 and 3000 a possible CC stretch from 1680 to 1630 and one or more C-H wagging peaks from 1000 to 600.
Sutton Gabriel da Silva and George V. Its value is 1635 for ester and 1681 for ketone CCSD6-311G dp or 17661848 ωB97XDaug-cc-pvQZ. The weight of the IR.
Correlation between bonding geometry and stretching mode wavenumber shifts Catherine. Alkane C-H bonds are fairly ubiquitous and therefore usually less useful in determining structure. The infrared spectra of six aqueous carboxylate anions have been calculated at the M05-2Xcc-pVTZ level of theory with the SMD solvent model and validated against experimental data from the literature over the region of 1700 cm-1 to 1250 cm-1.
Modelling the IR spectra of aqueous metal carboxylate complexes. The Wiberg bond order for the CO bond can be derived from the wavefunctions. νCO asym and a somewhat weaker symmetric CO 2 stretching vibration ie.
Table of IR Absorptions. This belief was validated with ab initio modeling for formate and acetate aqueous metal-carboxylate complexes. The double bond of the carbonyl group is therefore shorter and stronger and exhibits a larger stretching frequency.
This close agreement indicates that the carbonoxygen bond order in carboxylates is approximately 15. Up to 10 cash back The carboxylate content has been determined by infrared IR spectroscopy in different commercial salts of carboxylic acids and also in commercial and isolated samples of soil humic acids. This vibration is often mixed sometimes strongly with one or both aromatic.
Gas-phase spectra of a series of benzoate anions have been recorded and compared to condensed-phase spectra revealing the profound influence of the environment on the symmetric and antisymmetric. We have tested this principle with ab initio modeling for aqueous metal carboxylate complexes and have shown that it does indeed hold. A widely used principle is that shifts in the wavenumber of carboxylate stretching modes upon bonding with a metal centre can.
Carboxylic acids exist predominantly as hydrogen bonded dimers in condensed phases. The most useful characteristic bands of metal carboxylates are a strong asymmetric CO 2 stretching vibration ie. This is the opposite to that inferred from the carbonyl stretch and hence favours the bluered arrows over the green arrows.
Gas-phase spectra of a series of benzoate anions have. This region corresponds to the stretching modes of. This is the opposite to that inferred from the carbonyl stretch and hence favours the bluered arrows over the green arrows.
The Wiberg bond order for the CO bond can be derived from the wavefunctions. Absorption peaks above 3000 cm -1 are frequently diagnostic of unsaturation.

Ir Spectrum Interpreting Question R Chemhelp

How Range Peak Ir Spectrum For Carboxylic Acid Salts Ex Calcium Lactate
The C O Bond Part Iii Carboxylic Acids
22 2 Spectroscopy Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Chemistry Libretexts
Infrared Absorbance Spectroscopy Ir Mendelset
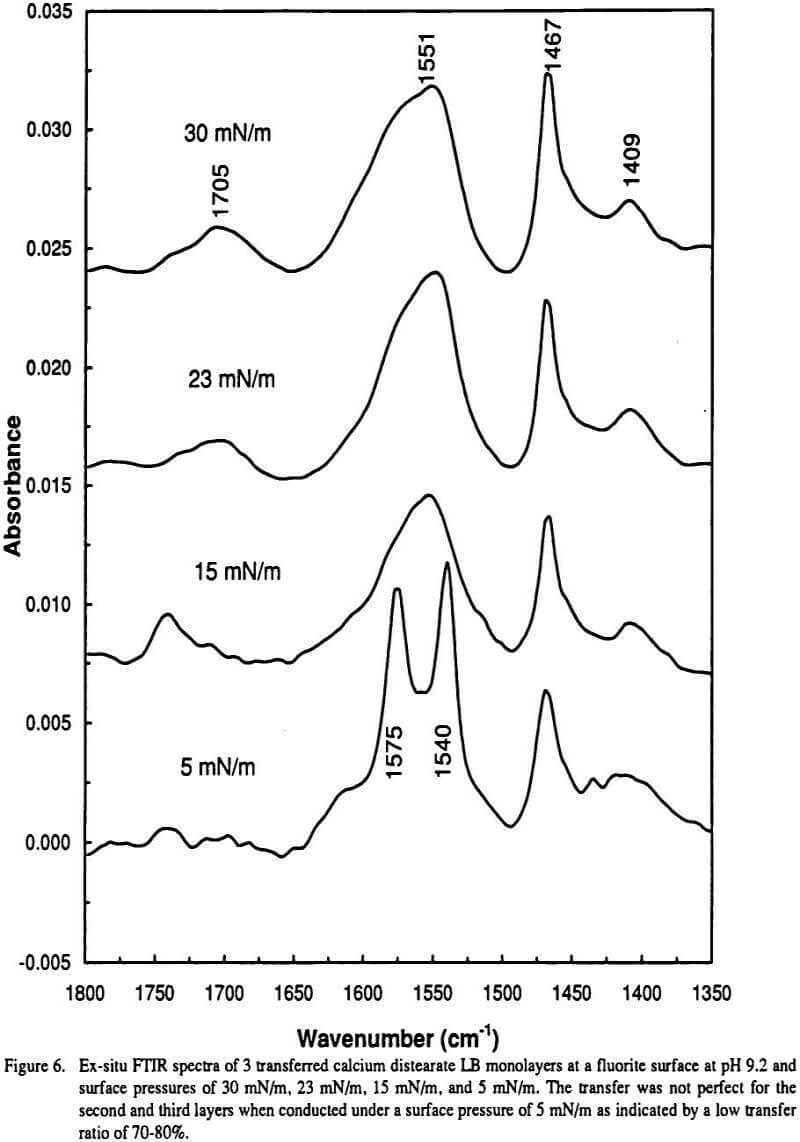
Ir Infrared Absorption Bands Of Carboxylate
The C O Bond Part Iii Carboxylic Acids

Infrared Spectrum Of Benzoic Acid C7h6o2 C6h5cooh Prominent Wavenumbers Cm 1 Detecting Functional Groups Present Finger Print For Identification Of Benzoic Acid Image Diagram Doc Brown S Advanced Organic Chemistry Revision Notes
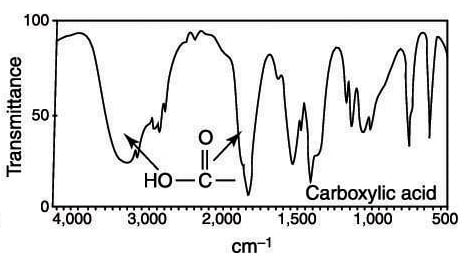
How To Identify Carbonyls Alkenes Alkynes And Aromatics In The Ir Spectrum Dummies
22 2 Spectroscopy Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Chemistry Libretexts

Infrared Spectrum Of Ethanoic Acid Prominent Wavenumbers Cm 1 Detecting Functional Groups Present Finger Print For Identification Of Ethanoic Acid Image Diagram Doc Brown S Advanced Organic Chemistry Revision Notes

How Range Peak Ir Spectrum For Carboxylic Acid Salts Ex Calcium Lactate
22 2 Spectroscopy Of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Chemistry Libretexts
21 3 Spectroscopy Of Carboxylic Acids Chemistry Libretexts
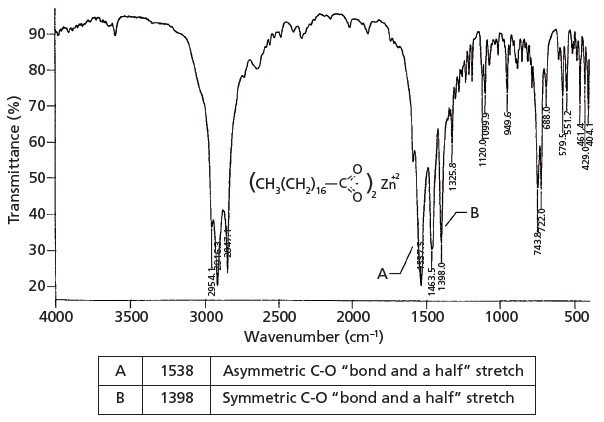
The Carbonyl Group Part V Carboxylates Coming Clean

Infrared Spectrum Of Butanoic Acid C4h8o2 Ch3ch2ch2cooh Prominent Wavenumbers Cm 1 Detecting Functional Groups Present Finger Print For Identification Of Butyric Acid Image Diagram Doc Brown S Advanced Organic Chemistry Revision Notes
Comments
Post a Comment